The results of the 2015 Greenwich Associates Exchange-Traded Funds Study show that results of Greenwich Associates debut Asian Exchange-Traded Funds Study show the potential for further growth.
Although overall investment in ETFs remains modest relative to total assets held by Asian institutions, the funds are being adopted for a wide variety of strategic and tactical tasks. The two most common applications for ETFs are strategic in nature: obtaining core investment exposures and international diversification within portfolios. These strategic uses of ETFs by Asian institutions are being adopted at a much faster pace than they were in North America and Europe.
ETFs in Asia first gained traction in institutional equity portfolios. Ninety-four percent of ETF users in the study employ ETFs in equity portfolios, and one-third use ETFs in fixed income. In the short-term, ETF growth will be driven by equities. Nearly 45% of institutional ETF users participating in the 2015 Asian ETF Study expect to increase equity ETF allocations in the coming year, and more than half of these institutions plan to boost allocations by 10% or more.
Over the longer term, Greenwich Associates expects ETF usage to expand in fixed income and other asset classes. To date, Asia appears to be following the pattern set in North America and Europe—institutions that first adopt ETFs in equity portfolios later expand usage to other areas.
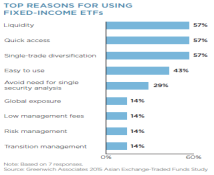
In fixed income, institutions around the world have started using ETFs to enhance portfolio liquidity amid declines in overall market liquidity. Institutions’ need for liquidity to support their sizable fixed-income portfolios could speed up the adoption of bond ETFs in Asia.
The study results reveal several areas where we can expect ETF usage in Asia to increase:
- ETFs as an alternative to futures. Half the ETF users in the study plan to replace an equity futures position with an ETF in 2016, and about 1 in 5 expect to replace a fixed-income futures position.
- Smart-beta ETFs take traction. Approximately one-quarter of the institutional ETF users in the study have started using non-market-cap-weighted/smart-beta ETFs. Nearly 30% of institutions that have started investing in these funds plan to increase smart-beta allocations in the year ahead, while over 60% of current users expect to invest in minimum volatility ETFs and over a quarter into single-factor and multi-factor ETFs.
- Increased use of ETFs in multi-asset strategies. The growing popularity of multi-asset investment strategies among investors globally is increasing ETF use among the asset managers offering these products. Nearly two-thirds of the Asian asset managers in the study use ETFs in multi-asset funds.
Institutions using ETFs for these and other reasons cite liquidity/trading volume, alignment with exposure needs, fund performance, and provider AUM as important criteria when selecting a specific fund for investment.
MethodologyGreenwich Associates interviewed a total of 52 Asia-based institutional investors, 31 of which were exchange-traded fund users and 21 were non-users, in an effort to track and uncover usage trends. The respondent base of ETF users in Hong Kong, Japan, Singapore, South East Asia, South Korea, and Taiwan included 16 institutional funds (corporate pensions, public pensions, foundations and endowments), 21 asset managers (firms managing assets to specific investment strategies/guidelines), and 15 insurance companies.